+: What Color Do Blue & Green Make?
What vibrant hues emerge when the serene embrace of blue intertwines with the verdant energy of green? The answer, far from being a simple one, unlocks a world of captivating colors, each with its own unique character and charm.
This isn't just a question of mixing paints; it's a journey into the heart of color theory, a dance between wavelengths, and a exploration of how these combinations resonate with our senses. Whether you're an artist, a designer, or simply a curious observer, the interplay of blue and green offers a spectrum of possibilities that are as diverse as they are beautiful.
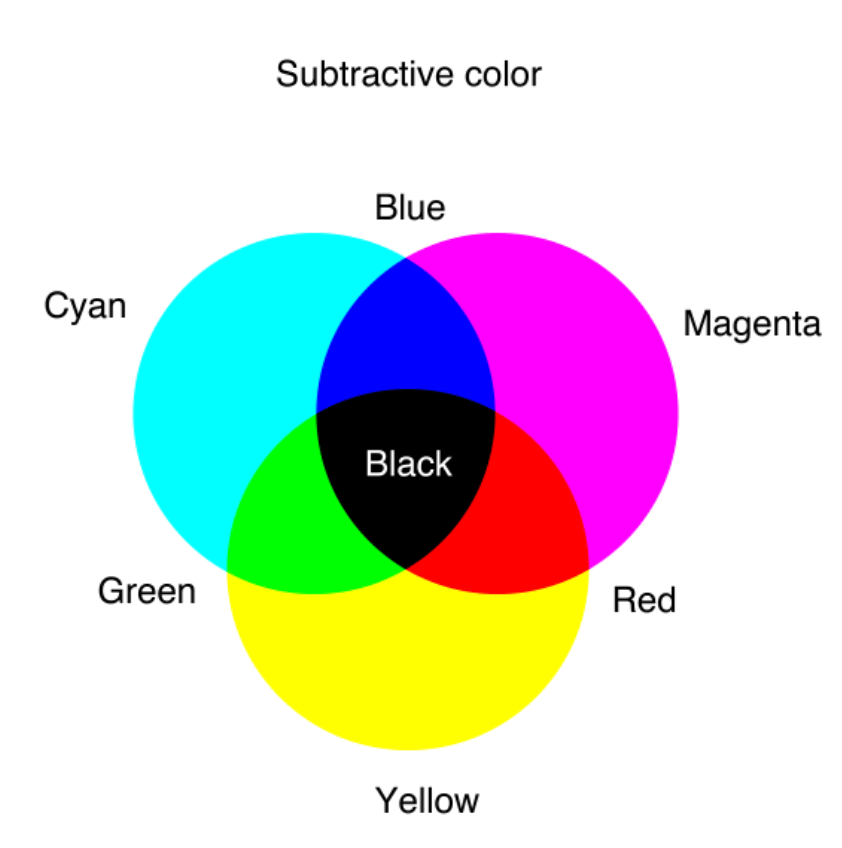
Let's begin by establishing the fundamentals. In the subtractive color system, the one we typically use for pigments, you combine colors to create new ones. Then, when blue and yellow are mixed, the resulting color is the secondary color green. While green is a mix of blue and yellow, and the color you get when mixing green and blue more closely resembles a shade of blue than a shade of green, because green itself is made up of 50% blue. However, the world of color is not so simply delineated.
Now, let's delve deeper into the fascinating world where the cool, calming essence of blue meets the lively, natural energy of green. Before, we establish that when mixing light, red and green make yellow, green and blue make cyan, and blue and red make magenta. The color you get when mixing green and blue more closely resembles a shade of blue than a shade of green, because green itself is made up of 50% blue. The ryb color wheel is something, In this model, the secondary colors are purple (red mixed with blue), orange (red mixed with yellow), and green (yellow mixed with blue).
The answer differs depending on the color model you work in. Blue and green can make a range of colors when mixed together. Let's break down what happens and the effects of different color mixing scenarios:
Mixing Paints (Subtractive Color)
When you mix blue and green pigments, such as in paint, you're working with the subtractive color system. The specific result depends on the ratio of each color.
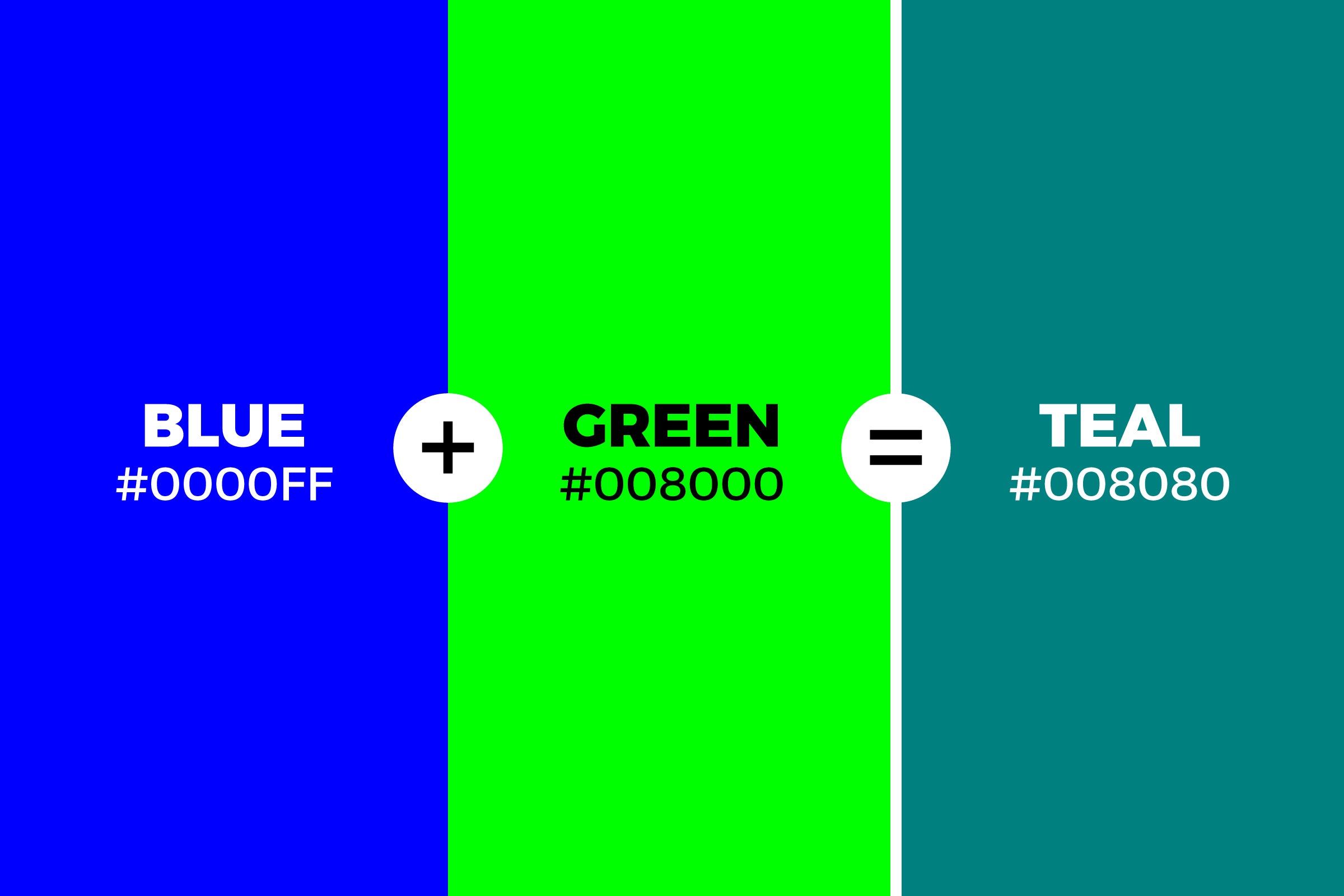
- Teal: Equal parts blue and green typically yield teal, a color that sits between blue and green on the color wheel.
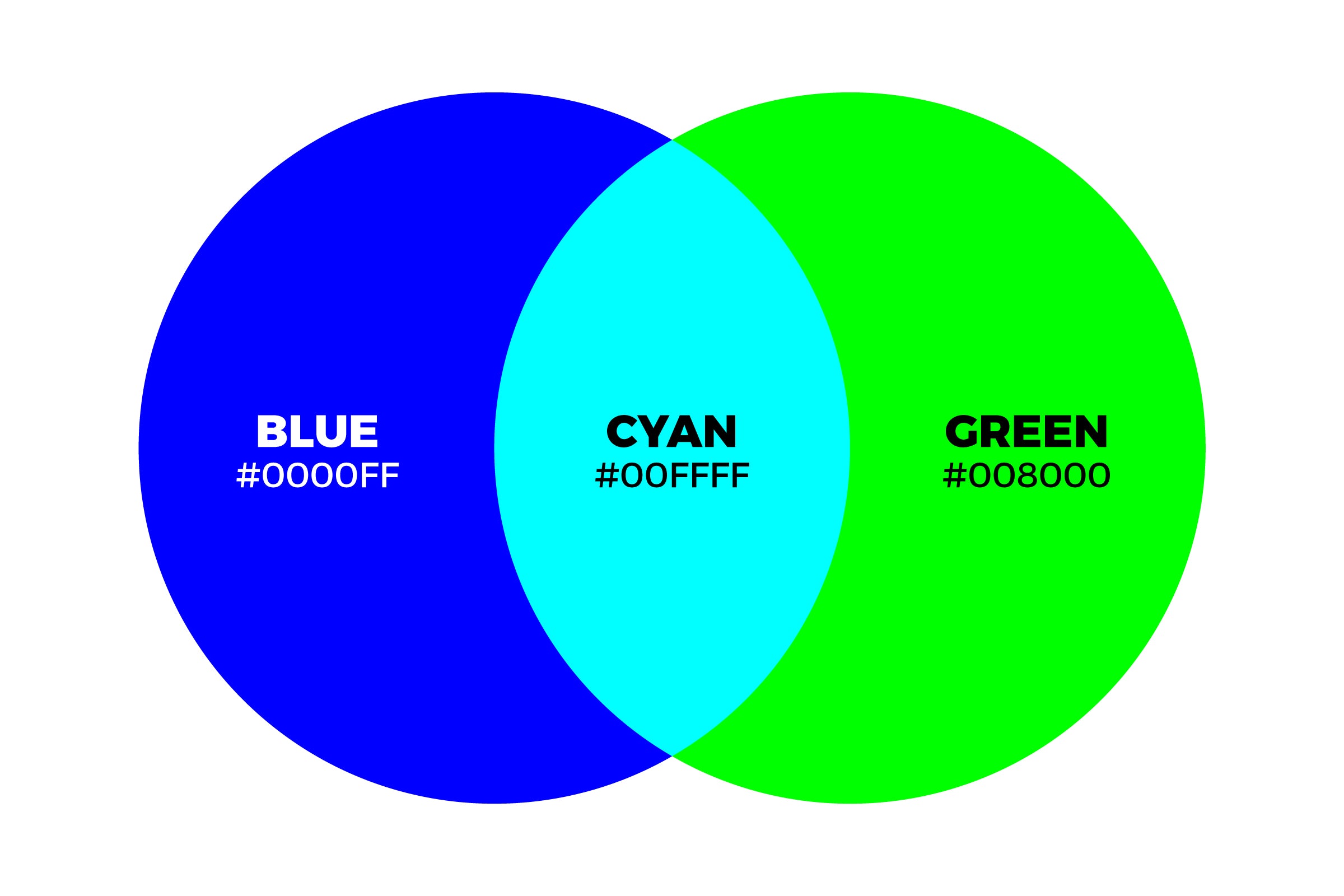
- Cyan: When green and blue are mixed in equal parts, they produce cyan.
- Turquoise: A blend of blue and green colors. You can make turquoise by mixing green and blue paint with a color bias toward green. For example, mix green with cyan, cobalt, ultramarine, or cerulean.
- Color Variation: The more blue you use, the more the mixture will lean towards blue. The more green you use, the more it will shift towards green.
Mixing Light (Additive Color)
With the additive color system, as when mixing light beams, it's different:
- Cyan: When blue and green light mix, you get cyan.
- RGB Model: In the world of light and screens, the primary colors are red, blue, and green (the rgb model), and all three colors together make white!
- Secondary Colors of Light: Mixing red, green, and blue light produce the secondary colors of light. Red and green make yellow, red and blue make magenta, and blue and green make cyan.
Tertiary Colors
Tertiary colors, which include teal, are created by mixing a primary color with a secondary color. Tertiary colors have a less intense, muddy, or neutralized look compared to the bold chromatic primaries. Six tertiary colors exist in total.
The Color Wheel
Understanding the color wheel helps to visualize relationships between colors:
- Primary Colors: Blue and green are two of the three primary colors.
- Secondary Colors: When you mix any two adjacent primary colors, the secondary colors are formed.
- Analogous Colors: Colors next to each other on any part of the color wheel, like blue, blue-green, and green, create a softer and less contrasted effect.
Color Psychology and Application
The combination of blue and green has many applications and appearances in art, design, nature, science, and more.
- Tranquility and Serenity: The combination of blue and green evokes feelings of tranquility, serenity, and nature.
- Home Decor and Design: Incorporating these two colors can bring a sense of calmness and balance.
Color Mixing Chart
A free online color mixing tool allows you to blend two or more colors: Red, blue, green, yellow, black, white, orange, grey, brown, purple, pink, or turquoise.
Additional Considerations:
Color Bias: Keep in mind the color bias of your pigments. For example, a green pigment might lean towards yellow or blue.
Opacity and Transparency: These properties of paint can also influence how the colors mix and appear.
Warm and Cool Colors
Knowing the difference between warm and cool colors can influence your color schemes and color mixing:
- Warm Colors: Reds, oranges, and yellows
- Cool Colors: Blues, greens, and violets
Neutral Colors: Black, white, and grays.
In the realm of colors, cyan, the child of blue and green light, is a testament to unity, harmony, and the extraordinary world of additive color mixing.
Key Takeaways:
- Teal, that is a mix of Blue and Green colors.
- Cyan, the color that blue and green make varies depending on your work environment and the type of blue and green you use in the mixture.
- Mixing blue and green yields a fascinating spectrum of colors, including turquoise, teal, and aqua, each with its own unique characteristics and emotional impact.
The next time you see a cyan hue, remember the wonderful dance of blue and green lights that makes it all possible.
Mixing blue and green is easy by following the subtractive color system. The strong properties of these two colors are enhanced and complement one another, rather than being subsumed and transformed, when mixed.